Double Materiality in ESG: A Competitive Edge in Sustainable Business
Table of content
Introduction
The introduction of double materiality in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting represents a breakthrough in sustainability and corporate accountability. This concept, also known as double materiality, integrates financial and environmental perspectives.
Compliance with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) significantly influences ESG reporting practices. Climate change and societal expectations are pressuring companies to focus not only on profits but also on protecting the environment, society, and long-term financial health.
According to the 2022 Global Reporting Initiative report, 92% of investors believe ESG factors are essential for assessing long-term investment returns, and 70% state that ESG influences their investment decisions.
In the ESG context, double materiality enables an evaluation of how a company’s operations affect its surroundings and how ESG-related risks and opportunities might impact its financial performance.
Not reporting ESG? Read more about the consequences [here].
Impact & financial materiality - what is Double Materiality Analysis?
Double materiality is a key concept in ESG reporting, referring to the analysis of a company’s impact on its environment and how ESG factors affect the company itself. The assessment incorporates impact materiality and financial materiality, forming a framework for sustainability reporting aligned with CSRD requirements. Additionally, the double materiality assessment process considers impacts on cash flows and future financial obligations.
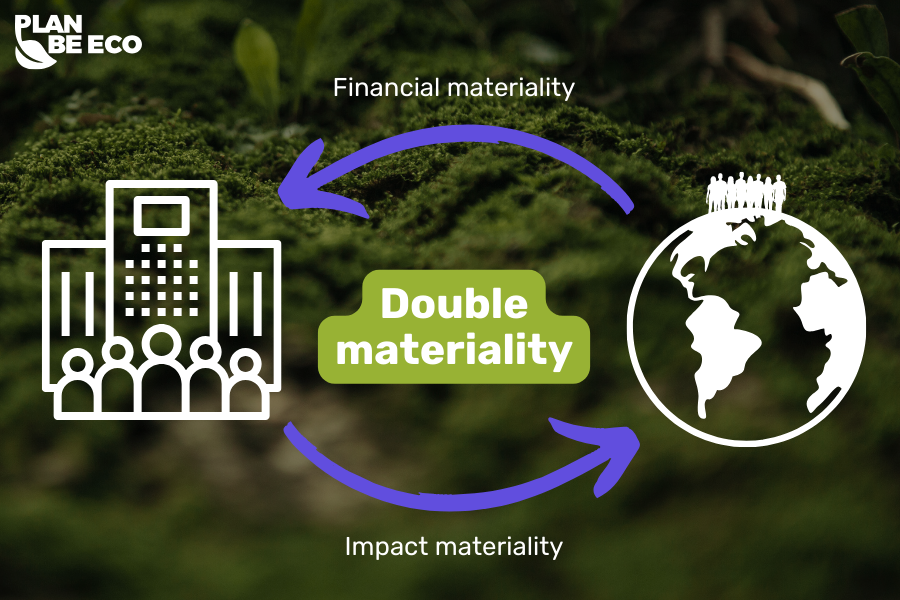
It can be defined as a dual-aspect evaluation process that considers both external and internal materiality. The first aspect, financial materiality, analyzes how environmental, social, and governance issues affect a company’s financial health. The second aspect, impact materiality, focuses on the company’s significant impact on the environment and society.
The European Commission, through the development of the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), has identified double materiality as a crucial component of new regulations. CSRD requires companies to transparently report ESG information, incorporating double materiality to help investors and stakeholders better assess ESG-related risks and opportunities.
Steps to Conduct a Double Materiality Assessment
A double materiality assessment involves several steps:
Identify Sustainability Issues
The materiality assessment process should consider factors relevant to stakeholders, such as environmental and social issues or sustainability matters. A study reveals that 68% of managers find identifying key ESG indicators one of the most challenging aspects of ESG reporting.Impact Assessment
This stage evaluates how a company’s activities impact both financial metrics and sustainability outcomes. Key areas include environmental impacts, social costs, and affected stakeholders across the value chain. Companies, especially those in high-risk sectors like fossil fuels, must assess their contributions to greenhouse gas emissions, climate risks, and future cash flows.Using frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), the assessment identifies financial implications and material financial effects that sustainability challenges may pose. This step ensures that both financial materiality and impact materiality are fully integrated into business planning.
Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement ensures the assessment reflects diverse perspectives and real-world concerns. This involves stakeholder interviews with key groups such as employees, investors, and local communities to identify critical factors and material sustainability matters.Engaging stakeholders helps align corporate objectives with societal expectations while addressing issues like gender and diversity policies or climate-related disclosures. This process builds trust and ensures transparency under frameworks like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). It reinforces credibility by integrating external input and strengthening relationships with stakeholders.

The Significance of Double Materiality in Practice
Double materiality enables companies to take a holistic view of their operations, combining financial perspective with social and environmental responsibility. It includes sustainability double materiality, allowing firms to identify material sustainability matters throughout their value chain. For example, in the financial services industry, incorporating double materiality broadens risk analysis related to lending risk.
By analyzing their environmental impact, companies can identify key ESG issues relevant to their operations and implement best practices for sustainable development.
Examples of companies that have implemented double materiality
According to a survey by PwC, 40% of companies in Europe have completed a double materiality analysis and 46% are in the process of doing so. According to a PwC study, 40% of European companies have already completed a double materiality analysis and 46% are in the process of doing so. The increased importance of sustainability and ESG regulation means that many companies are seeing the benefits of implementing these principles, contributing to better risk management and building trust among stakeholders.
Siemens
Siemens employs advanced double materiality assessments, focusing on technological innovations that reduce environmental impact and enhance energy efficiency. Analyses based on the double materiality approach have allowed the company to identify areas generating sustainability impacts and improve strategies addressing environmental and social costs.
Volkswagen
Volkswagen’s double materiality analysis revealed high risks associated with emissions, accelerating its electrification strategy and achieving a 15% reduction in emissions.
Unilever
In its 2023 report, Unilever identified the impact of climate change on operations, such as lower agricultural yields due to extreme weather. The company assessed the risk of rising raw material costs and the potential of sustainable agricultural practices.
Procter & Gamble
P&G applies double materiality to analyze the health impacts of its products and their environmental effects, reporting efforts to reduce plastic use and improve production energy efficiency.

Why Is Sustainability Reporting Important?
- Understanding Risks and Opportunities
ESG reporting enables companies to identify not only the negative impacts of their actions but also the risks and opportunities related to sustainability. Supporting financial materiality assessments helps companies better understand the financial implications of their actions and enhance their strategic approach to ESG issues. - Supporting Business Strategy
Understanding double materiality enhances the ability to adapt business strategies, increasing resilience to risks and maximizing benefits from responsible actions. - Building Stakeholder Trust
Transparent ESG reporting can increase trust among stakeholders like investors, customers, and employees, essential for long-term business success.
Benefits of ESG Reporting for Companies and Stakeholders

Adopting double materiality in ESG reporting helps companies better monitor sustainability efforts and evaluate the regulatory impact of ESG on their business models. Companies implementing effective ESG strategies often achieve better financial performance, strengthening relationships with investors and suppliers while building a positive public image.
A study by the Warsaw Stock Exchange (GPW) found that 40% of respondents believe companies incorporating ESG into their strategies can achieve better financial results. ESG-aligned companies are also included in high-performing ESG indices, which group enterprises adhering to high standards in environmental care, social responsibility, and corporate governance.
Similarly, a CDP report indicates that companies with robust ESG strategies experience 25% lower capital costs, making them more stable and attractive to investors.
For investors and stakeholders, double materiality provides a clearer understanding of the company’s full impact — financially, environmentally, and socially. Employees, in turn, may see ESG efforts as a reinforcement of ethical values and a genuine commitment to the company’s long-term growth.

Challenges and the Future of Double Materiality
Despite its benefits, conducting a double materiality analysis involves challenges, including difficulties in identifying ESG indicators and assessing the company’s environmental and social impacts. The introduction of ESRS aims to standardize reporting requirements, making it easier for businesses to incorporate double materiality.
Companies must align their ESG reporting with CSRD requirements, preparing for future global regulations. Double materiality, as a new standard of reporting, demands collaboration among businesses, investors, and regulators to create a comprehensive and transparent approach to sustainability reporting.
According to a Deloitte report, 65% of companies worldwide will need to integrate ESG reporting into their strategies by 2030, significantly impacting their market value and capital access.

Plan Be Eco: Supporting ESG and Double Materiality Reporting
Innovative tools like Plan Be Eco are emerging to simplify ESG reporting. This market leader provides advanced ESG solutions, enabling companies to meet regulatory requirements while equipping them with the knowledge to handle reporting independently.
Plan Be Eco offers expert-backed tools that ensure high-quality analyses compliant with current standards like ESRS and CSRD. By collaborating with double materiality specialists, Plan Be Eco supports companies in conducting comprehensive impact and financial materiality assessments, facilitating strategic decision-making.
Their tools enable efficient risk management, ESG challenge identification, and competitive advantage discovery, helping businesses build long-term value and sustainability.
Summary
Double materiality and ESG reporting are now not just regulatory requirements but also a foundation for risk management and value creation in modern business. Implementing a double materiality framework aligned with European Sustainability Reporting Standards allows companies to better prepare for new challenges such as climate risks and the impact perspective.
Companies successfully implementing double materiality — evaluating both their impact on the environment and society and the financial relevance of ESG issues — can better prepare for evolving regulations and stakeholder expectations. In the long term, this approach fosters reputation building and enhances trust among investors, customers, employees, and other key groups.
Integrating ESG principles into operational and strategic activities also better prepares companies for climate risks and opportunities arising from increasing emphasis on sustainability, often leading to improved financial performance.
![plan_be_eco_[New guidelines The European Commission recommends reducing emissions by 90% by 2040]_eng](https://planbe.eco/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/plan_be_eco_New-guidelines-The-European-Commission-recommends-reducing-emissions-by-90-by-2040_eng.png)
