How Tech Companies Approach ESG Reporting

With its rapid growth and innovation, the tech industry faces unique ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) challenges related to data privacy, electronic waste, and energy consumption. As technology becomes increasingly central to our lives, tech companies are expected to address these concerns through comprehensive ESG reporting, a tool that ensures transparency and accountability. This report helps companies monitor their ESG performance, meet stakeholder expectations, and align their business strategies with sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Table of Contents
Key Findings
According to Climate Home News, by 2040, the global ICT sector is expected to contribute to 14% of total global greenhouse gas emissions. This figure would be on par with the current emissions of the second-largest emitter worldwide, the United States.
Electronics Hub reported that Samsung has the largest carbon footprint among major tech companies, releasing 20.1 million metric tons of CO₂e annually.
Recently Microsoft reported that its emissions are 30% higher today than in 2020, reports Yahoo Finance.
The carbon footprint of the tech industry

The tech industry’s carbon footprint is substantial, driven by the massive energy requirements of data centers, device manufacturing, and global supply chains. For instance, the information and communications technology (ICT) sector is responsible for around 2-3% of global carbon emissions, on par with the aviation industry. The rapid expansion of cloud computing, AI, and blockchain technologies has increased energy consumption within this sector.
Data Centers
These facilities are among the biggest contributors to the tech sector’s carbon footprint. Data centers globally consumed about 200 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity in 2022, more than the entire energy consumption of some countries, such as Argentina. However, tech companies are investing in energy-efficient infrastructure. For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has optimized its data centers, making them up to 4.1 times more energy-efficient than traditional on-premises IT operations, which can reduce carbon emissions by up to 99% when workloads are optimized on the cloud.
Big Tech Emissions
Large companies like Amazon, Google, and Apple are key players in driving tech-related emissions. In 2021, Amazon alone was responsible for 16.1 million metric tons of CO₂ emissions. Despite pledging to reach net zero by 2040, the company saw an 18% increase in its emissions from 2020 to 2021 due to a surge in business during the pandemic. Google and Microsoft have also been criticized for their significant carbon footprints, although they are investing heavily in renewable energy solutions.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
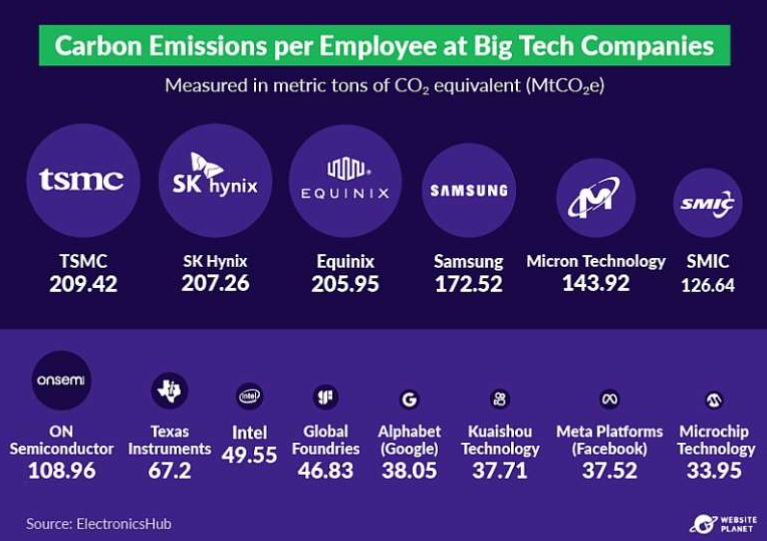
This industry has an especially high carbon intensity. Companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), responsible for 92% of global semiconductor production, generate substantial emissions. TSMC alone produces over 200 metric tons of CO₂ per employee annually. Semiconductor production is energy-intensive, with processes requiring high temperatures and electricity—much of which is sourced from fossil fuels, especially in regions like Asia where these facilities are concentrated.
The tech industry is making strides toward reducing its carbon footprint, with increased investment in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and more efficient technologies. As of 2023, companies like Amazon have deployed over 24,000 electric delivery vehicles and delivered 680 million packages using electric transportation, cutting down on vehicle emissions. Furthermore, companies are focusing on sustainable product designs and packaging, with Amazon reducing single-use plastics by 43% since 2015.
Despite these efforts, tech companies must continue to innovate in energy efficiency, ethical sourcing, and sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact and meet global climate targets.
Navigating ESG in the Technology Sector

As technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the modern world, tech companies must take responsibility for their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. While driving global innovation, the industry faces significant environmental challenges, from the energy-intensive operations of data centers to the ecological impact of manufacturing and disposing of electronic devices.
For example, data centers alone consume around 200 terawatt-hours of electricity annually, accounting for nearly 1% of global electricity consumption. With AI, cloud computing, and blockchain technologies rapidly expanding, energy demand in the sector is projected to grow significantly.
In addition to energy use, the electronic waste (e-waste) generated by tech products represents a growing environmental concern. In 2021, global e-waste reached 57.4 million metric tons, yet only about 17.4% was properly recycled. This highlights the urgent need for tech companies to implement circular economy models by designing products that are easier to repair, recycle, and reuse.
Tech companies must prioritize sustainability efforts, embracing energy efficiency and sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact. Initiatives such as transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving data center energy efficiency, and incorporating sustainable materials into product design are essential steps forward. By doing so, companies can significantly lower their carbon footprint while maintaining their reputation as innovation leaders.
A tech company’s commitment to sustainable products and ethical business practices can be highlighted through detailed sustainability reports. These reports are often based on recognized frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), which provide clear metrics on ESG performance.
By adhering to these standards, companies offer transparency in addressing ESG principles. This transparency fosters trust among stakeholders and mitigates risks related to regulatory compliance and market perception. Companies with strong ESG performance tend to experience lower volatility and reduced risk in the long term.

Corporate Strategy and ESG Initiatives
For tech giants like Google, Apple, and Microsoft, integrating ESG into corporate strategy involves not only managing risks but also seizing opportunities to foster positive changes. These companies are leading the way by setting ambitious sustainability targets, such as achieving net-zero emissions or even becoming carbon-negative. Microsoft, for instance, has committed to being carbon-negative by 2030 and aims to remove all of its historical carbon emissions by 2050. Google, on the other hand, has been carbon neutral since 2007 and is working toward operating on carbon-free energy 24/7 by 2030.
By aligning with global sustainability efforts, tech companies can innovate in ways that meet climate change goals while also driving business development. For example, investments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to optimize energy use, predict supply chain disruptions, and improve resource efficiency. Read how the popularity of artificial intelligence affects the climate.
Moreover, AI can play a pivotal role in promoting ethical practices, as seen in the development of ethical AI frameworks that prioritize social responsibility and human rights. Companies like IBM and Salesforce are at the forefront of ensuring that AI is used to benefit society, avoiding biases and negative impacts on vulnerable communities.
ESG initiatives across the technology industry are reshaping how companies operate. For example, a software company might focus on minimizing its energy consumption in cloud services, as seen with Amazon Web Services (AWS), which is working to power all of its data centers with 100% renewable energy by 2025. Meanwhile, hardware manufacturers like Dell and HP are addressing the issue of electronic waste by incorporating recycled materials into their products and offering take-back programs for used devices.
Companies that succeed in embracing ESG and integrating it into their business model demonstrate not only good corporate ethics but also a long-term commitment to sustainability goals, creating a competitive advantage in a marketplace increasingly driven by conscious consumers.

The Role of Governance and Accountability
Strong governance plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of ESG efforts within the tech sector. Effective governance ensures that ESG principles are not treated as an afterthought but are integrated into the core of business strategy. This requires the board of directors and senior leadership to be fully engaged in overseeing the company’s ESG performance. Many tech companies are appointing Chief Sustainability Officers (CSOs) or creating ESG committees to ensure that sustainability goals are met and that corporate social responsibility (CSR) is embedded into daily operations.
Annual reports should reflect the company’s progress in meeting its sustainability targets, offering a transparent view of the company’s impact on the environment and society. These reports not only highlight achievements but also identify areas for improvement, allowing stakeholders to hold companies accountable. For instance, Apple’s Environmental Progress Report details its initiatives to eliminate carbon emissions across its supply chain by 2030.
Moreover, ESG criteria must be woven into the fabric of a tech company’s decision-making process. This includes risk management strategies that account for the company’s supply chain, ensuring that materials and services are sourced ethically and sustainably. Companies like Intel and Samsung have made significant strides in developing ethical supply chains, working to eliminate conflict minerals, and ensuring fair labor practices throughout their operations. Developing ethical supply chains not only reduces environmental harm but also promotes social equity and supports communities where tech companies operate, contributing to positive social impact.

Tech Companies and the Future of ESG
Looking ahead, the technology sector will continue to evolve as it responds to the growing demands for sustainability. With consumers, investors, and regulators increasingly prioritizing ESG performance, tech companies must adapt to maintain their competitive edge. From advancing energy-efficient data centers to creating sustainable products with a minimal carbon footprint, tech companies will be at the forefront of shaping a more sustainable future. Companies like Tesla, which focuses on developing renewable energy solutions and electric vehicles, showcase how technological innovation can drive both business success and environmental progress.
Technology itself will remain a key driver in addressing global ESG challenges, offering solutions that promote a positive impact for future generations. Innovations in clean energy, smart cities, and circular economy practices will be crucial in helping the world meet its sustainability goals. As tech companies continue to leverage their capabilities, they will have the unique opportunity to lead other sectors in reducing environmental footprints and fostering social equity.
Ultimately, social and governance ESG factors are becoming non-negotiable elements of corporate strategy for tech companies. By continuing to focus on ESG and maintaining a clear commitment to corporate social responsibility, these companies not only enhance their financial performance but also contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world.
The future of information technology lies in its ability to harmonize technological innovation with global sustainability efforts, ensuring a lasting, positive impact on the planet and society as a whole.

Cooperation with Plan Be Eco
Given the growing importance of sustainability and corporate responsibility, partnering with Plan Be Eco is an excellent step for tech companies seeking to enhance their ESG efforts. Plan Be Eco specializes in calculating the carbon footprint of companies and products, preparing comprehensive ESG reports, and developing decarbonization strategies. Additionally, it offers expert consulting services and provides educational support to business leaders on sustainable practices and corporate responsibility.
With their support, tech companies can better manage their environmental impact, optimize their supply chains, implement energy-efficient solutions, and create more transparent sustainability reports.
Plan Be Eco’s expertise in sustainability allows tech companies to not only meet regulatory requirements but also build stronger relationships with their stakeholders. As ESG becomes increasingly crucial to corporate strategy, partnering with a firm like Plan Be Eco helps businesses stay ahead of market demands, reduce risks, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Summary
The tech industry, known for its rapid growth and innovation, faces distinct ESG challenges, such as data privacy, electronic waste, and energy consumption. Tech companies increasingly incorporate ESG principles into their business models to enhance sustainability and accountability. By embracing comprehensive ESG reporting, following guidelines from the Global Reporting Initiative, and integrating ESG into corporate strategy, tech companies can manage risks, improve financial performance, and strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
Technological innovation, energy-efficient practices, and ethical supply chains are crucial for reducing environmental impact and contributing to social responsibility. As the technology sector evolves, companies that prioritize ESG factors will play a key role in creating a more sustainable and equitable future for society and future generations.
